Product Description
Ferric citrate monohydrate CAS Number is 2338-05-8, also known as ferric citrate, is a chemical product that has been used for many years. It is a structurally indeterminate complex. According to the literature, the method for synthesizing Ferric citrate monohydrate is to use citric acid and ferric hydroxide as raw materials, add citric acid to iron hydroxide, heat at a temperature lower than 60℃, evaporate to a slurry, and coat it on a glass plate. Above, dry at low temperature until a small piece is formed, and peeling is obtained. This conventional Ferric citrate monohydrate CAS Number 2338-05-8 can only be called crude iron citrate, which is purple-brown and thin scaly. The method of preparing iron citrate used for many years should be said to be very random. The final product is mainly composed of iron citrate. There are no clear requirements for the various conditions of the preparation process and the performance of the final product, resulting in the product being soluble in water but not easily dissolved. Later, some researchers adjusted the bulk density of the solid finished iron citrate and made solid iron citrate of different densities. The obtained product has extremely fine voids inside and has a large surface area, so it is easily dissolved by water. It solves the problem that the medicinal solubility of iron citrate is small.
The preparation method of the pharmaceutical grade iron citrate is prepared by mixing iron hydroxide as a starting material with 1.05 equivalent of citric acid containing one crystal water, and then adding purified water, and then reacting in a water bath of 60-70℃, The reaction was carried out for about 48 to 2 hours, and centrifuged at 4000 rpm to remove suspended particles. The supernatant was heated and evaporated at 60℃ to remove water, and then spread on a flat plate and dried to obtain crude granules. The obtained crude granules were immersed in 95% ethanol at room temperature or lower for 2 hours, and the residual citric acid was dissolved therein. Filtration and ethanol elution gave pharmaceutical grade iron citrate.
At present, iron citrate CAS Number 2338-05-8 is mainly a food additive for iron supplementation or a nutritional supplement. For example, it can be added to biscuits, calcium milk powder and wheat flour, and India is also used for salt. In addition, there are reports on the treatment of hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic renal failure. Iron citrate has been reported as a new phosphorus-binding agent for hemodialysis patients with chronic renal failure. It can be taken at the same time as food. The phosphate in the gastrointestinal tract reduces the absorption of phosphate in the gastrointestinal tract, thereby reducing hyperphosphatemia in patients with chronic renal failure. Because of the cardiovascular calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease, there is a view that hyperphosphatemia is an influencing factor of cardiovascular calcification in patients with ESRD (end-stage renal failure), and hyperphosphatemia is involved in vascular ectopic calcification of ESRD. However, the blood phosphorus and blood calcium of ESRD patients with partial vascular calcification are still normal. In addition, vascular calcification associated with atherosclerosis is not directly related to human blood phosphorus levels. Therefore, cardiovascular calcification of chronic renal failure is a multi-pathogenic, multi-pathway, very complex process involving multiple molecules, and the effect of blood phosphorus levels on calcification is unknown.
It has been found that iron citrate can effectively prevent arterial calcification in rats caused by vitamin D3 and nicotine, which proves that iron citrate can effectively inhibit cardiovascular ectopic calcification by intervening in the process of soft tissue calcification, and it is possible Reverse the occurrence of ectopic calcification.
Thera. Category: Nutritional Supplement
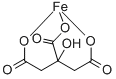
Cas No.: 2338-05-8
Synonyms:Iron(III) citrate tribasic monohydrate,Ferric citrate monohydrate;IRON(lll) CITRATE, hydrate, tech-95;FERRIC CITRATE NHYD;Iron citrate tetrahydrate;Ferric Citrate, Powder;Iron(Ⅲ) Citrate n-Hydrate;2,3-propanetricarboxylicacid,2-hydroxy-ironsalt;IRON (III) CITRATE, GREEN
MF: C6H5FeO7
NW:244.94
Assay: ≥99%
Packing:Export worthy packing
Material Safety Data Sheet:Available on request

.png) Contact Now
Contact Now
